Popular Keywords
- About Us
-
Research Report
Research Directory
Semiconductors
LED
Consumer Electronics
Emerging Technologies
- Selected Topics
- Membership
- Price Trends
- Press Center
- News
- Events
- Contact Us
Recent Posts
- [News] Foxconn Reportedly Secures the Lion’s Share for NVIDIA’s GB300, with New Products Set to Debut in 1H25
- [News] Semiconductor Silicon Wafer and Silicon Carbide Giants Build New Plants!
- [News] U.S. and Australia Seek Countermeasures, Impact of China’s Critical Material Ban Expected to Wane in the Long Run
- [News] SK hynix Rumored to Deliver Major HBM Order to Broadcom in 2025
- [News] TSMC Rumored to Begin FOPLP Production with Smaller Substrates, with Mini Lines Prepared by 2026
Recent Comments
Archives
- December 2024
- November 2024
- October 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- June 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- March 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
- April 2021
- March 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- July 2020
- June 2020
- May 2020
- April 2020
- March 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- July 2019
- June 2019
- May 2019
- April 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- July 2018
- June 2018
- May 2018
- April 2018
- March 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- July 2017
- June 2017
- May 2017
- April 2017
- March 2017
- February 2017
- January 2017
- December 2016
- November 2016
- October 2016
- September 2016
- August 2016
- July 2016
- June 2016
- May 2016
- April 2016
- March 2016
- February 2016
- December 2015
- November 2015
- October 2015
- September 2015
- August 2015
- July 2015
- June 2015
- May 2015
- April 2015
- March 2015
- January 2015
- December 2014
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- July 2014
- June 2014
- May 2014
- April 2014
- February 2014
- January 2014
- December 2013
- November 2013
- October 2013
- September 2013
- August 2013
- July 2013
- June 2013
- May 2013
- April 2013
- March 2013
- February 2013
- January 2013
- December 2012
- November 2012
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- July 2012
- May 2012
- April 2012
- March 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- July 2011
- June 2011
- May 2011
- April 2011
- March 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- November 2010
- October 2010
- September 2010
- August 2010
- July 2010
- June 2010
- May 2010
- April 2010
- March 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
- December 2009
- November 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- July 2009
- May 2009
- April 2009
- March 2009
- November 2008
- October 2008
- September 2008
- August 2008
- March 2008
- January 2008
- December 2007
Categories
- 5G Technologies
- AR / VR
- Artificial Intelligence
- Automotive Technologies
- Broadband & Home Network
- Cloud / Edge Computing
- Consumer Electronics
- DataTrack-EN
- DataTrack-TW
- Display
- Display Supply Chain
- Display Technologies
- DRAM
- Emerging Technologies
- Energy
- IC Design
- IC Manufacturing, Package&Test
- Industry 4.0
- IoT
- IR LED / VCSEL / LiDAR Laser
- LCD
- LED Backlight
- LED Chip & Package
- LED Demand / Supply Data Base
- LED Display
- LED Lighting
- Lithium Battery and Energy Storage
- Macroeconomics
- Market Today
- Market Trends
- Micro LED / Mini LED
- Monitors / AIO
- NAND Flash
- Notebook Computers
- OLED
- Optical Semiconductors
- Others
- Panel Industry
- Products News
- Semiconductors
- server
- Smartphones
- Solar PV
- Tablets
- Telecommunications
- TVs
- Upstream Components
- Wafer Foundries
- Wearable Devices
- 市場日報
- 未分類
- 趨勢洞察
Meta
Articles
News

[New] The Reality of Micro LED Unveiled – Infinite Opportunities, Yet Initial Capacity Demand Remains Low
Ennostar, a Taiwanese group focusing on the R&D and manufacturing of Micro LED, LED and compound semiconductor, has announced on January 19th a NTD 670 million (roughly USD 21.36 million) sale of the planned Micro LED production facility in Zhunan, Taiwan. Its subsidiary, EPISTAR, is anticip...
News

[News] Subsidies from the U.S. Legislation “NAPMP” Potentially Expected to Cover IC Substrates
The U.S. Department of Commerce has initiated the "National Advanced Packaging Manufacturing Program (NAPMP) ," with materials and substrates being the first subsidized areas. Due to the close collaboration between IC testing and IC substrates, it is not ruled out that the IC substrate industry coul...
News

[News] China’s Chip Equipment Imports Surge 14% to Nearly USD 40 Billion in 2023
As companies increased their investments in 2023, the Chinese semiconductor industry actively expanded, leading to a substantial increase in the import volume of China's chip manufacturing equipment. According to Bloomberg’s report citing official Chinese customs data, the import value of equip...
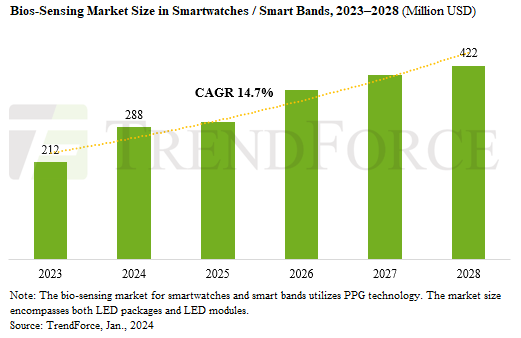
Benefited from Enhancing Bio-Sensing Technology, the Market in Wearable Device Applications to Reach US$422 Million, Says TrendForce
Jan. 22, 2024 ---- In a pivotal ruling, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit has decided against Apple in its patent dispute with Masimo, mandating a halt in sales of the Series 9 and Ultra 2 in the US due to their blood oxygen features. This decision pushes Apple to potentially remove ...
News

[News] Expert Insights on NVIDIA’s AI Chip Strategy – Downgraded Version Targeted for China, High-End Versions Aimed Overseas
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang has reportedly gone to Taiwan once again, with reports suggesting a recent visit to China. Industry sources believe NVIDIA is planning to introduce downgraded AI chips to bypass U.S. restrictions on exporting high-end chips to China. Huang's visit to China is seen as an effo...
- Page 290
- 586 page(s)
- 2928 result(s)





